To be continued
Quantum Neural Networks
- Basic idea of QNN
- Architecture of QNN
- Training QNN
- Barren Plateaus in QNN
- QCNN
- DQNN
1.1. Basic idea of QNN
1.1.1. Architecture of QNN
We introduce architecture of QNN by comparing it with the classical artificial neural network
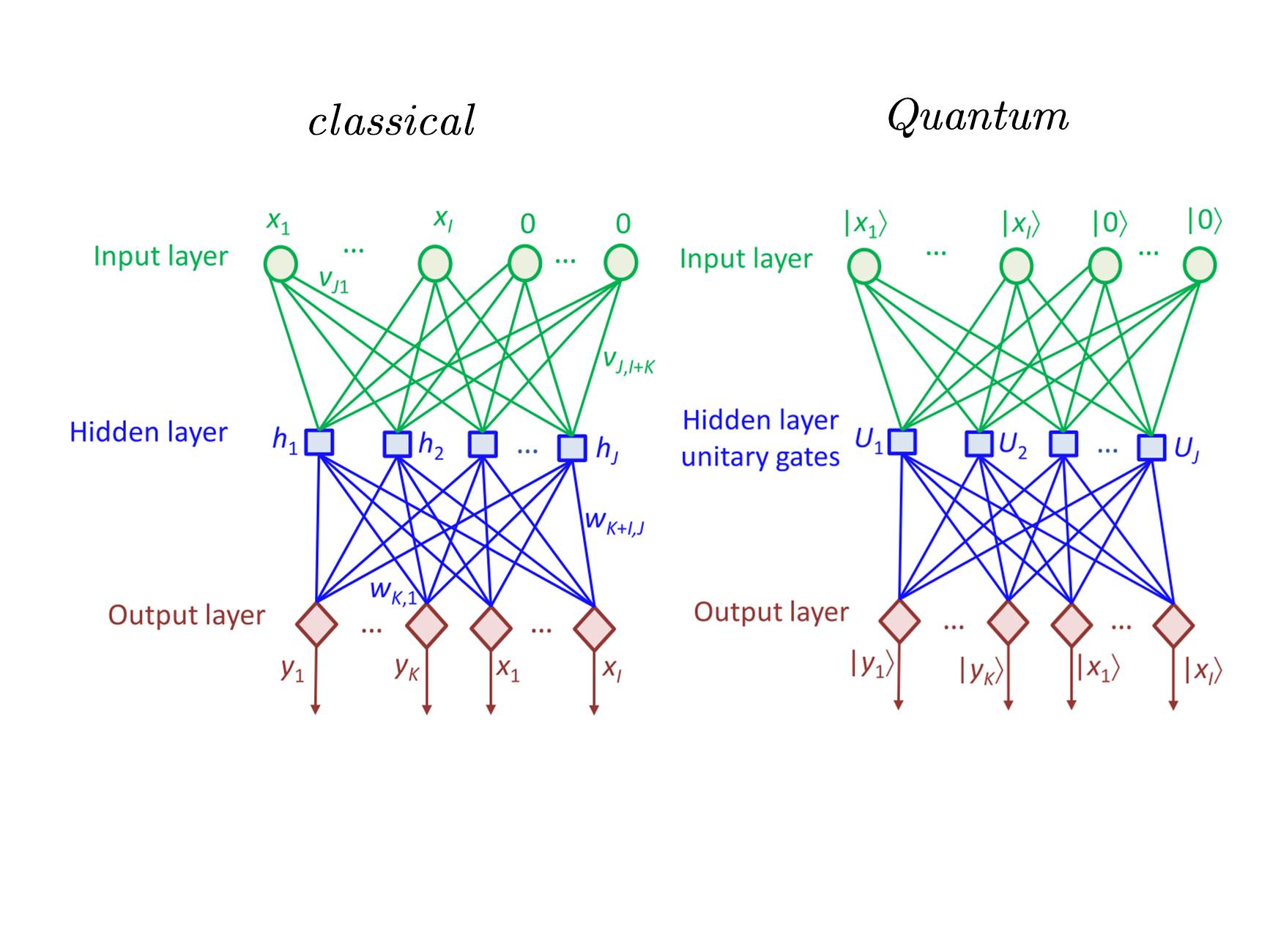
1.data input
2 neural network
neural network unitary quantum gates
The action of the th unitary operator on qubits can be represented by: where
- represent the Pauli matrices.
3 cost function
where
- is dependent on the unitary operator parameters
- represents the labels at the output neurons for the th training instance .
4 gradient descent
We can use the gradient descent to update the parameters in the th unitary matrix as follows:
1.1.2. Training QNN
- Ricks, Bob, and Dan Ventura. "Training a quantum neural network." Advances in neural information processing systems 16 (2003).
- Beer, Kerstin, et al. "Training deep quantum neural networks." Nature communications 11.1 (2020): 1-6.
- Zhang, Kaining, et al. "Toward trainability of deep quantum neural networks." arXiv:2112.15002 (2021).
To be continued
1.2. Barren plateaus in QNN
- arXiv:1803.11173 (2018) Barren plateaus in quantum neural network training landscapes
Exponential decay of variance.
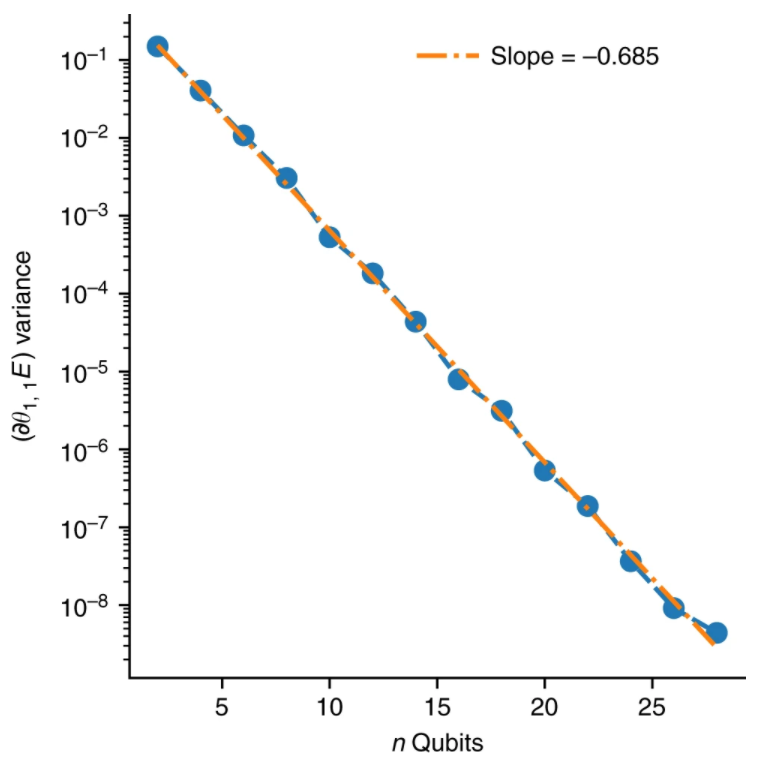
The sample variance of the gradient of the energy for the first circuit component of a two-local Pauli term plotted as a function of the number of qubits on a semi-log plot. As predicted, an exponential decay is observed as a function of the number of qubits, , for both the expected value and its spread. The slope of the fit line is indicative of the rate of exponential decay as determined by the operator
variance of measurements where The average value of the gradient where the gradient of the objective function
1.3. QCNN
Absence of Barren Plateaus in Quantum Convolutional Neural Networks
1.4. Reference
What is QNN
- A review of Quantum Neural Networks: Methods, Models, Dilemma arXiv:2109.01840
- Kak, S. (1995). "On quantum neural computing". Advances in Imaging and Electron Physics. 94: 259–313. doi):10.1016/S1076-5670(08)70147-270147-2)
- Efficient Learning for Deep Quantum Neural Networks (2020) arXiv:1902.10445
- Training deep quantum neural networks Nat Commun 11, 808 (2020)
- On quantum neural networks 2021 arXiv:2104.07106
- early definition of QNN & modern definition of QNN
What problem QNN advantage in?
- The Power of Quantum Neural Networks 2020 arXiv:2011.00027
- Power of data in quantum machine learning 2021 arXiv:2011.01938
What is (Barren Plateau)in QNN ?
- Barren plateaus in quantum neural network training landscapes
- Cost function dependent barren plateaus in shallow parametrized quantum circuits Nature Communications 12, 1791 (2021)
- Trainability of Dissipative Perceptron-Based Quantum Neural Networks arxiv.2005.12458
What make(Barren Plateau)?
- explain
- arXiv: 2010.15968 Entanglement Induced Barren Plateaus
What is QCNN
2019 Harve
- Nature Physics 15,1273-1278(2019) Quantum convolutional neural networks
- A Tutorial on Quantum Convolutional Neural Networks (QCNN) arxiv.2009.09423
- TensorFlow implements QCNN
absence Barren Plateau in QCNN